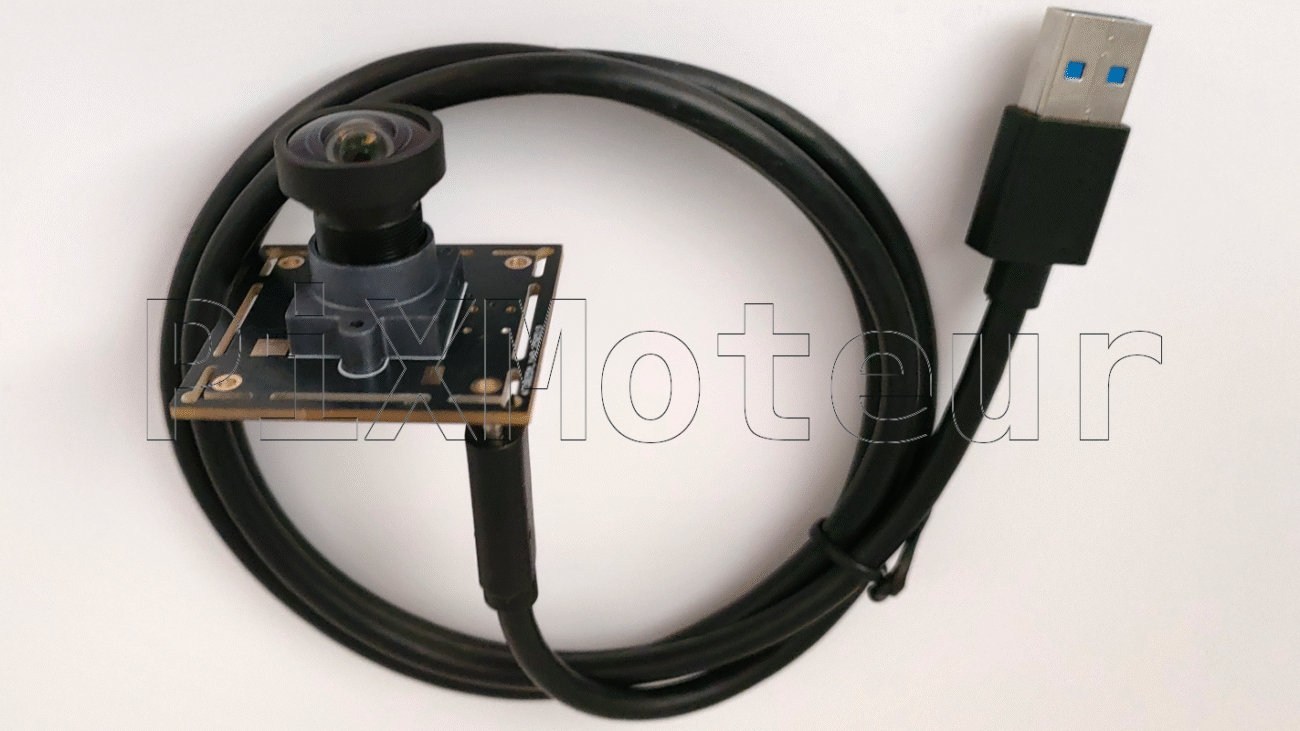
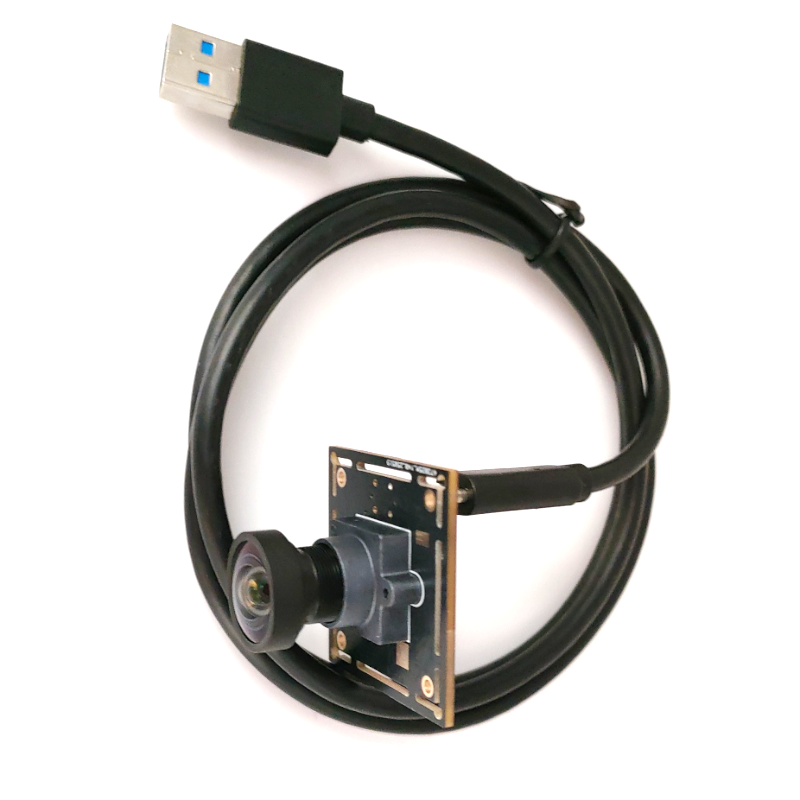
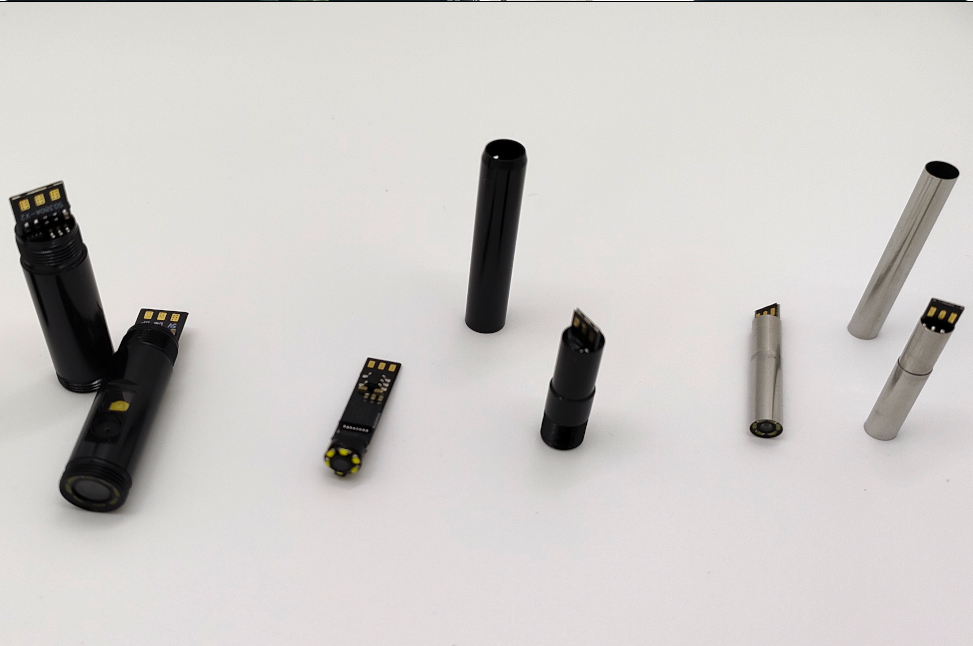
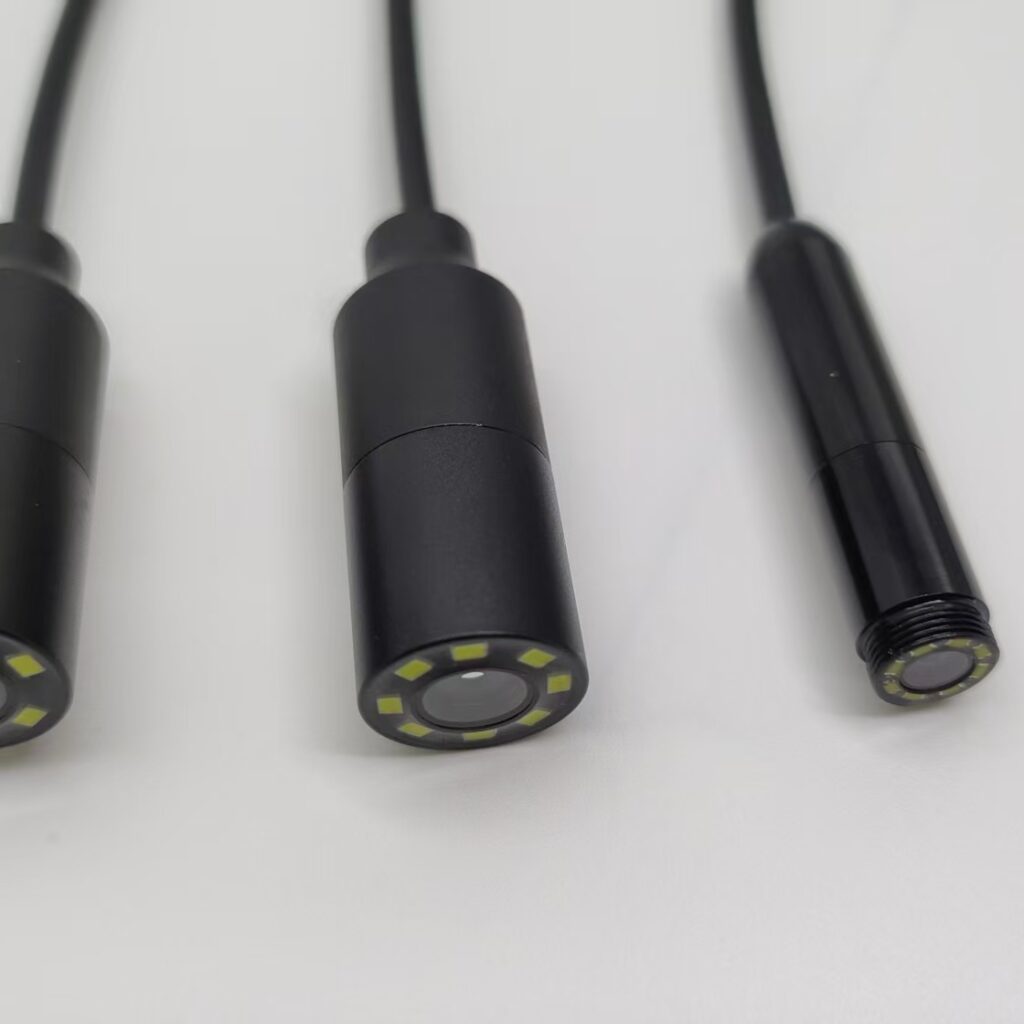
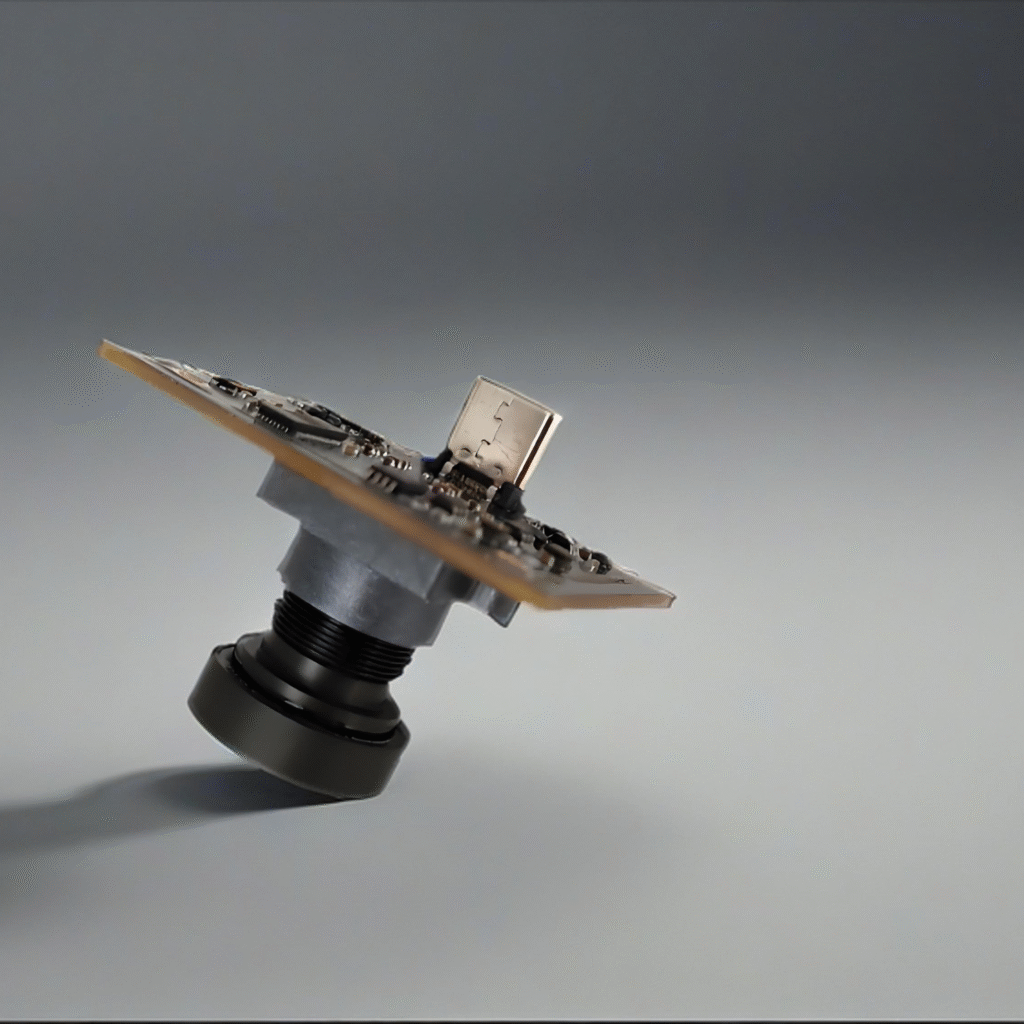
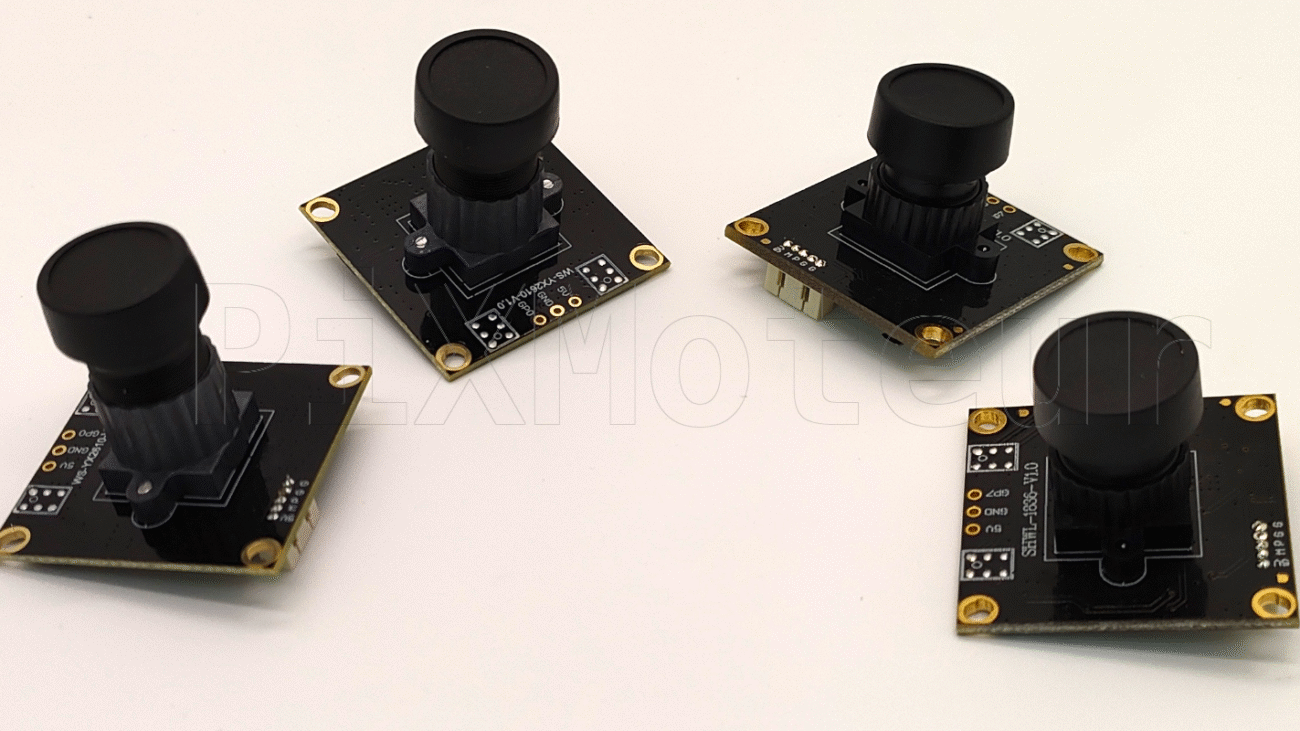
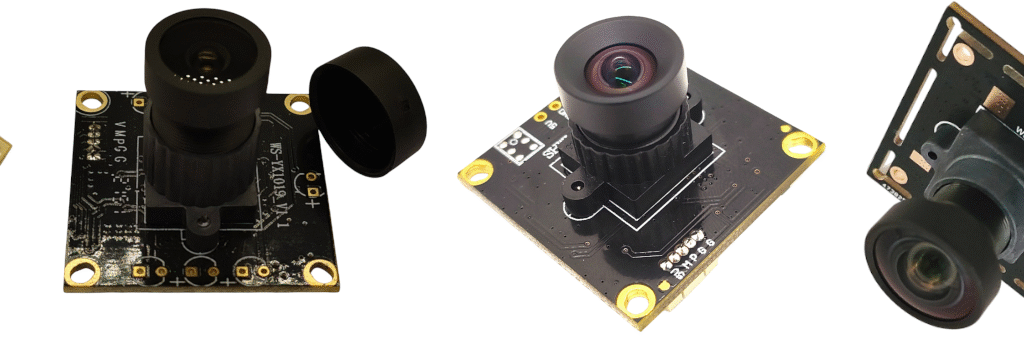
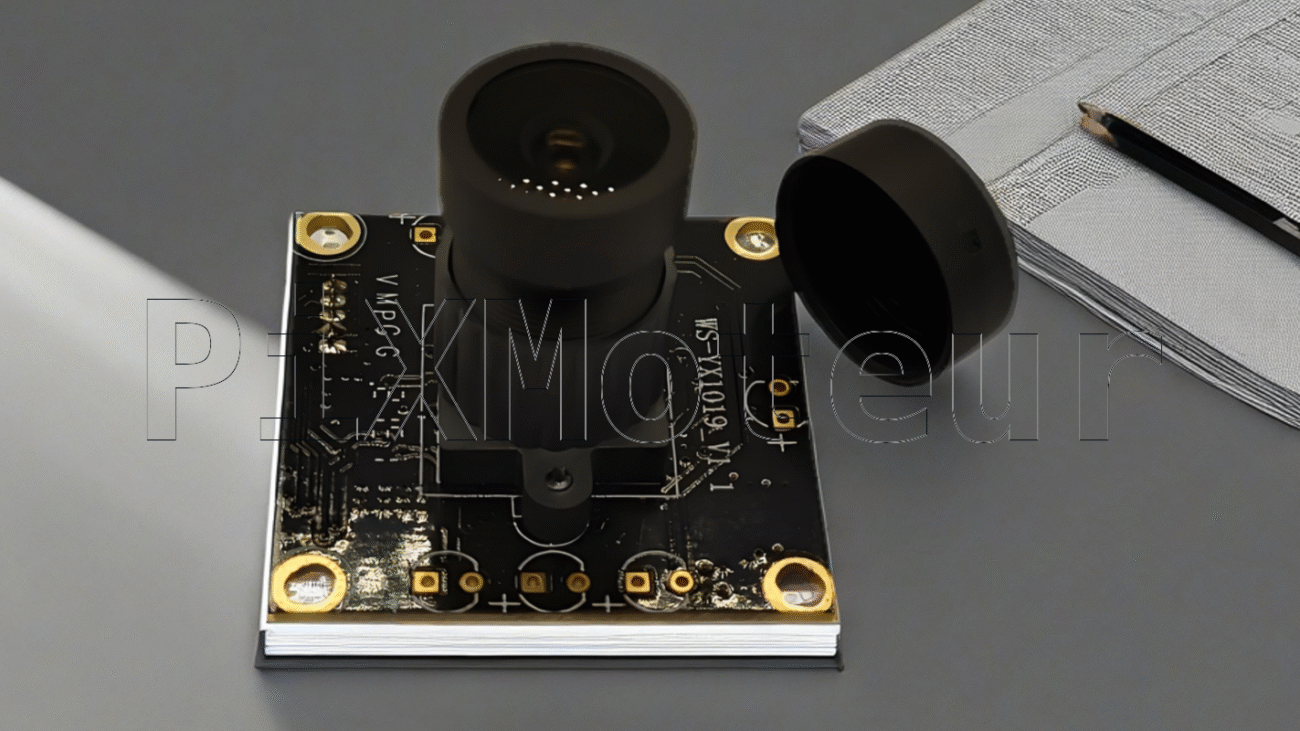
The Fishing Camera is a compact, rugged underwater camera module designed for anglers, researchers, and inspection professionals. Combining a wide-angle lens, HD LCD display, and intelligent features such as voice prompt and Wi‑Fi connectivity, it delivers a convenient, high-quality view into underwater environments. The unit supports 50 m cable length, up to 8 hours of continuous operation, and accepts OEM & ODM requests with full customization.
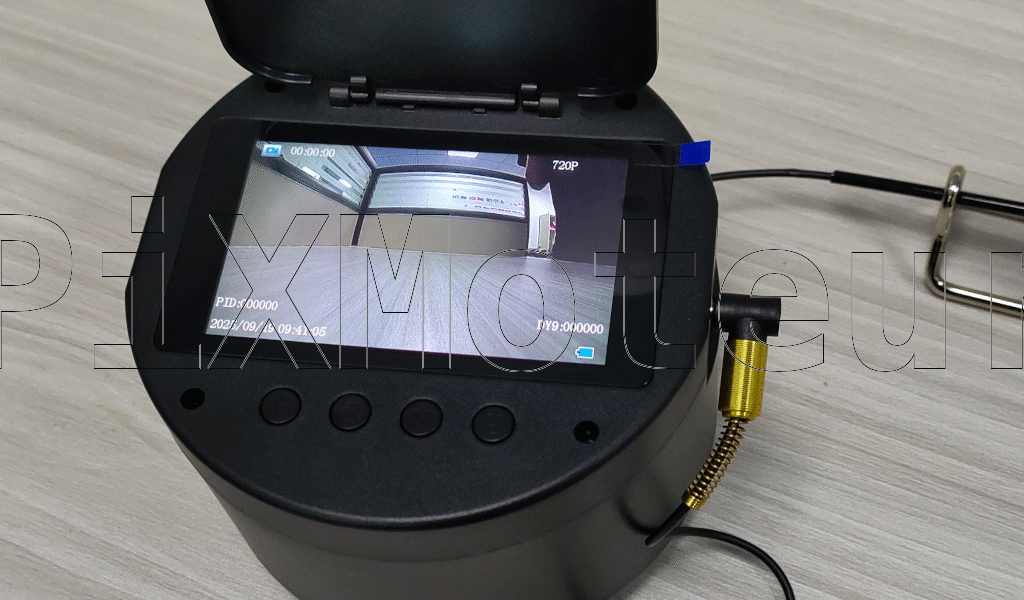

Fishing Camera
Key Features
- Wide-angle camera: Captures a broad field of view to monitor fish behavior and underwater structures more effectively than narrow lenses.
- 50 m coiled cable: Flexible, space-saving coiled cable design that extends to 50 meters for deep-water use while staying tangle-resistant and easy to stow.
8 hours working time: Long battery life for extended fishing trips or inspection sessions without frequent recharging.- HD LCD with protector: Built-in high-definition display for live monitoring and playback, protected by a durable screen guard to resist scratches and impacts. - Video playback: On-device playback lets you review recorded footage immediately on the HD LCD—no need to transfer files first.
- Voice prompt: Spoken feedback for status updates (power, recording, connection) for hands-free operation and better situational awareness.
- Wi‑Fi connection: Stream live video to smartphones or tablets, transfer files wirelessly, and control camera functions via a companion app.
- Coiled cable: Enhances portability and reduces cable wear; retraction helps avoid snags and makes deployment/retrieval faster.
- Accepts OEM & ODM: Full customization available for lens specification, housing materials, cable length, connector types, UI language, branding, and feature sets.
Fishing Camera Typical Use Cases
- Recreational fishing: Spot and monitor fish behavior, check bait placement, and evaluate structure.
- Scientific research: Record and review underwater observations for behavioral or habitat studies.
- Boat and hull inspection: Inspect keels, propellers, and hard-to-reach underwater components.
- Aquaculture monitoring: Check pen conditions, fish health, and feed activity.
- Search and recovery: Assist short-range search of submerged areas where visibility allows.